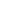Splay trees are self-adjusting binary search trees i.e., they adjust their nodes after accessing them. So, after searching, inserting or deleting a node, the tree will get adjusted.
Splay trees put the most recently accessed items near the root based on the principle of locality; 90-10 "rule" which states that 10% of the data is accessed 90% of the time, other 90% of data is only accessed only 10% of the time.

Thus, there is a 90% chance that the elements near the root of a splay tree are going to be accessed in an operation.
Let's learn how these trees adjust nodes on accessing them.
Splaying
"Splaying" is a process in which a node is transferred to the root by performing suitable rotations. In a splay tree, whenever we access any node, it is splayed to the root. It will be clear with the examples given in this chapter.
There are few terminologies used in this process. Let's learn about those.
Zig-Zig and Zig-Zag
When the parent and the grandparent of a node are in the same direction, it is zig-zig.

When the parent and the grandparent of a node are in different directions, it is zig-zag.

Whenever we access a node, we shift it to the root by using suitable rotations. Let's take the following example.

Here, we have performed a single right rotation and a single rotation is termed as "zig".

"zig-zag" consists of two rotations of the opposite direction. Take a look at the following example.

Let's take a look at the following example in which we have accessed the node R.

So, we have performed two single rotations of the same direction to bring the node at the root. This is "zig-zig".
Let's take a look at some examples.

A splay tree is not always a balanced tree and may become unbalanced after some operations.
Let's write a code to splay a node to the root.
Code for Splaying
We will start by passing the tree (T) and the node which is going to be splayed (n).
SPLAY(T, n)
We have to splay the node n to the root. So, we will use a loop and perform suitable rotations and stop it when the node n reaches to the root.
SPALY(T, n)
while n.parent != NULL //node is not root
...
Now, if the node n is the direct child of the root, we will just do one rotation, otherwise, we will do two rotations in one iteration.
SPALY(T, n)
while n.parent != NULL //node is not root
if n.parent == T.root //node is child of root, one rotation
if n == n.parent.left //left child
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, n.parent)
else //right child
LEFT_ROTATE(T, n.parent)
else //two rotations
...

To perform two rotations, we will first set a variable p as the parent of n and a variable g as grandparent of n.
SPALY(T, n)
while n.parent != NULL //node is not root
if n.parent == T.root //node is child of root, one rotation
...
else //two rotations
p = n.parent
g = p.parent

Now, we just have to do the rotations.
SPALY(T, n)
while n.parent != NULL //node is not root
...
else //two rotations
...
if n.parent.left == n and p.parent.left == p //both are left children
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, g)
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, p)
else if n.parent.right == n and p.parent.right == p //both are right children
LEFT_ROTATE(T, g)
LEFT_ROTATE(T, p)
else if n.parent.right == n and p.parent.left == p
LEFT_ROTATE(T, p)
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, g)
else
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, p)
LEFT_ROTATE(T, g)
SPLAY(T, n)
while n.parent != NULL //node is not root
if n.parent == T.root //node is child of root, one rotation
if n == n.parent.left //left child
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, n.parent)
else //right child
LEFT_ROTATE(T, n.parent)
else //two rotations
p = n.parent
g = p.parent
if n.parent.left == n and p.parent.left == p //both are left children
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, g)
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, p)
else if n.parent.right == n and p.parent.right == p //both are right children
LEFT_ROTATE(T, g)
LEFT_ROTATE(T, p)
else if n.parent.right == n and p.parent.left == p
LEFT_ROTATE(T, p)
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, g)
else
RIGHT_ROTATE(T, p)
LEFT_ROTATE(T, g)
Searching in a Splay Tree
Searching is just the same as a normal binary search tree, we just splay the node which was searched to the root
SEARCH(T, n, x)
if x == n.data
SPLAY(T, n)
return n
else if x < n.data
return search(T, n.left, x);
else if x > n.data
return search(T, n.right, x);
else
return NULL
This is the same code that of a binary search tree, we are just splaying the node to root if it is found - if x == n.data → SPLAY(T, n).
Insertion in a Splay Tree
We normally insert a node in a splay tree and splay it to the root.

INSERT(T, n)
temp = T.root
y = NULL
while temp != NULL
y = temp
if n.data < temp.data
temp = temp.left
else
temp = temp.right
n.parent = y
if y==NULL
T.root = n
else if n.data < y.data
y.left = n
else
y.right = n
SPLAY(T, n)
Deletion in a Splay Tree
To delete a node in a splay tree, we first splay that node to the root.

After this, we just delete the root which gives us two subtrees.

We find the largest element of the left subtree and splay it to the root.

Lastly, we attach the right subtree as the right child of the left subtree.

Let's write the code for deletion.
Code for Deletion in Spaly Tree
We will first store the left and right subtrees in different variables.
DELETE(T, n)
left_subtree = new splay_tree
right_subtree = new splay_tree
left_subtree.root = T.root.left
right_subtree = T.root.right
if left_subtree.root != NULL
left_subtree.root.parent = NULL
if right_subtree.root != NULL
right_subtree.root.parent = NULL
Then we will find the maximum of the left subtree and splay it to the root.
if left_subtree.root != NULL
m = MAXIMUM(left_subtree, left_subtree.root)
SPLAY(left_subtree, m)
After that, we will make the right subtree the right child of the new root of the left subtree.
if left_subtree.root != NULL
...
left_subtree.root.right = right_subtree.root
T.root = left_subtree.root
If there is no left subtree, we will make right subtree the new tree.
if left_subtree.root != NULL
...
else
T.root = right_subtree.root
DELETE(T, n)
left_subtree = new splay_tree
right_subtree = new splay_tree
left_subtree.root = T.root.left
right_subtree = T.root.right
if left_subtree.root != NULL
left_subtree.root.parent = NULL
if right_subtree.root != NULL
right_subtree.root.parent = NULL
if left_subtree.root != NULL
m = MAXIMUM(left_subtree, left_subtree.root)
SPLAY(left_subtree, m)
left_subtree.root.right = right_subtree.root
T.root = left_subtree.root
else
T.root = right_subtree.root
- C
- Python
- Java
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node {
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
struct node *parent;
}node;
typedef struct splay_tree {
struct node *root;
}splay_tree;
node* new_node(int data) {
node *n = malloc(sizeof(node));
n->data = data;
n->parent = NULL;
n->right = NULL;
n->left = NULL;
return n;
}
splay_tree* new_splay_tree() {
splay_tree *t = malloc(sizeof(splay_tree));
t->root = NULL;
return t;
}
node* maximum(splay_tree *t, node *x) {
while(x->right != NULL)
x = x->right;
return x;
}
void left_rotate(splay_tree *t, node *x) {
node *y = x->right;
x->right = y->left;
if(y->left != NULL) {
y->left->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent;
if(x->parent == NULL) { //x is root
t->root = y;
}
else if(x == x->parent->left) { //x is left child
x->parent->left = y;
}
else { //x is right child
x->parent->right = y;
}
y->left = x;
x->parent = y;
}
void right_rotate(splay_tree *t, node *x) {
node *y = x->left;
x->left = y->right;
if(y->right != NULL) {
y->right->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent;
if(x->parent == NULL) { //x is root
t->root = y;
}
else if(x == x->parent->right) { //x is left child
x->parent->right = y;
}
else { //x is right child
x->parent->left = y;
}
y->right = x;
x->parent = y;
}
void splay(splay_tree *t, node *n) {
while(n->parent != NULL) { //node is not root
if(n->parent == t->root) { //node is child of root, one rotation
if(n == n->parent->left) {
right_rotate(t, n->parent);
}
else {
left_rotate(t, n->parent);
}
}
else {
node *p = n->parent;
node *g = p->parent; //grandparent
if(n->parent->left == n && p->parent->left == p) { //both are left children
right_rotate(t, g);
right_rotate(t, p);
}
else if(n->parent->right == n && p->parent->right == p) { //both are right children
left_rotate(t, g);
left_rotate(t, p);
}
else if(n->parent->right == n && p->parent->left == p) {
left_rotate(t, p);
right_rotate(t, g);
}
else if(n->parent->left == n && p->parent->right == p) {
right_rotate(t, p);
left_rotate(t, g);
}
}
}
}
void insert(splay_tree *t, node *n) {
node *y = NULL;
node *temp = t->root;
while(temp != NULL) {
y = temp;
if(n->data < temp->data)
temp = temp->left;
else
temp = temp->right;
}
n->parent = y;
if(y == NULL) //newly added node is root
t->root = n;
else if(n->data < y->data)
y->left = n;
else
y->right = n;
splay(t, n);
}
node* search(splay_tree *t, node *n, int x) {
if(x == n->data) {
splay(t, n);
return n;
}
else if(x < n->data)
return search(t, n->left, x);
else if(x > n->data)
return search(t, n->right, x);
else
return NULL;
}
void delete(splay_tree *t, node *n) {
splay(t, n);
splay_tree *left_subtree = new_splay_tree();
left_subtree->root = t->root->left;
if(left_subtree->root != NULL)
left_subtree->root->parent = NULL;
splay_tree *right_subtree = new_splay_tree();
right_subtree->root = t->root->right;
if(right_subtree->root != NULL)
right_subtree->root->parent = NULL;
free(n);
if(left_subtree->root != NULL) {
node *m = maximum(left_subtree, left_subtree->root);
splay(left_subtree, m);
left_subtree->root->right = right_subtree->root;
t->root = left_subtree->root;
}
else {
t->root = right_subtree->root;
}
}
void inorder(splay_tree *t, node *n) {
if(n != NULL) {
inorder(t, n->left);
printf("%d\n", n->data);
inorder(t, n->right);
}
}
int main() {
splay_tree *t = new_splay_tree();
node *a, *b, *c, *d, *e, *f, *g, *h, *i, *j, *k, *l, *m;
a = new_node(10);
b = new_node(20);
c = new_node(30);
d = new_node(100);
e = new_node(90);
f = new_node(40);
g = new_node(50);
h = new_node(60);
i = new_node(70);
j = new_node(80);
k = new_node(150);
l = new_node(110);
m = new_node(120);
insert(t, a);
insert(t, b);
insert(t, c);
insert(t, d);
insert(t, e);
insert(t, f);
insert(t, g);
insert(t, h);
insert(t, i);
insert(t, j);
insert(t, k);
insert(t, l);
insert(t, m);
delete(t, a);
delete(t, m);
inorder(t, t->root);
return 0;
}